English Corner
Advantages and Disadvantages of Foreign Direct Investment
Foreign direct investment (FDI) has become one of the most influential drivers of economic development in the modern global economy. As countries open their markets and integrate into international trade, foreign investors increasingly view global expansion as a strategic priority. From manufacturing to real estate, from technology to consumer services, international firms explore investment opportunities outside their domestic borders to strengthen their competitive positions and gain access to new markets.
FDI brings a wide range of benefits, such as creating employment, boosting productivity, improving infrastructure, and facilitating technology transfer. However, it also involves challenges including risks of over-dependency on foreign companies, negative environmental impacts, and potential crowding out of domestic enterprises. To evaluate the full picture, it is necessary to analyze both the advantages and disadvantages of foreign direct investment in global, national, and local contexts.
This article explores the concept of FDI, the common forms it takes, and a detailed breakdown of its positive and negative impacts on host countries, home countries, and multinational corporations (MNCs). By understanding this topic, governments and business leaders can design policies and strategies that ensure FDI truly contributes to sustainable and inclusive economic growth.
What Is Foreign Direct Investment?
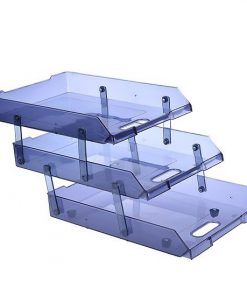
Foreign direct investment refers to the process in which a company or individual from one country invests in a business or productive assets located in another country with the intention of gaining long-term management control or significant influence. This distinguishes FDI from portfolio investment, where investors simply purchase financial assets like stocks or bonds without controlling the business.
FDI can occur in several forms:
- Greenfield investments: Establishing entirely new business facilities or factories in a foreign country.
- Mergers and acquisitions (M&A): Purchasing or merging with an existing foreign company to enter the market quickly.
- Joint ventures: Partnering with a local company to share ownership, resources, and risks.
- Reinvestment of profits: Using income generated from foreign operations to expand investment.
These forms of FDI shape how benefits and risks are distributed among economies and business participants.
Advantages of Foreign Direct Investment
FDI can significantly transform a developing or emerging economy, especially when domestic capital and advanced knowledge are limited. Below are the major advantages of foreign direct investment:
-
Economic Growth and Capital Inflow
One of the most important benefits of FDI is the injection of capital into the host country. This capital helps fund infrastructure projects, new factories, and business expansion—developments that local governments or companies might not be able to finance alone.
Increased investment leads to increased output, supporting higher GDP growth. For many developing nations, FDI serves as a key pillar for economic modernization.
-
Job Creation and Improved Workforce Skills
FDI brings employment opportunities to local people:
- New factories and major construction projects require large labor forces.
- Service-sector investments create jobs in retail, tourism, and technology.
- Workers acquire new skills from international companies’ professional training programs.
As workers gain experience, the domestic labor force becomes more productive and globally competitive.
-
Technology Transfer and Innovation
Foreign companies often introduce advanced technologies, modern business practices, and innovative production methods. This can:
- Improve manufacturing quality and efficiency
- Increase productivity in multiple industries
- Encourage local firms to adopt new technologies
Technology transfer helps accelerate a country’s transition from low-value to high-value industries.
-
Enhanced Infrastructure Development (Advantages and Disadvantages of Foreign Direct Investment)
Investment in transportation, logistics, energy, and communication infrastructure often accompanies major FDI projects. Better infrastructure benefits all businesses, including domestic companies, and improves the quality of life for citizens.
-
Increased Exports and Access to Global Markets
Multinational corporations usually produce goods not only for local consumption but also for export. As a result:
- Export revenue increases
- Trade balance improves
- Host countries become more integrated with international value chains
FDI can turn developing markets into manufacturing hubs serving global customers.
-
Competition Stimulation and Domestic Industry Improvement
The arrival of foreign companies increases market competition. Local firms must:
- Improve product quality
- Upgrade technology
- Enhance service offerings
- Manage costs more efficiently
Competition pushes the entire economy toward better performance and innovation.
-
Government Revenue and Public Finance Support
Foreign enterprises contribute to the national budget through:
- Corporate taxes
- Income taxes from new employees
- Licensing fees
- Customs duties
These funds help governments improve public services such as education, healthcare, and infrastructure.
-
Consumer Benefits and Higher Standards of Living
FDI introduces new products, better customer service, and more choices at competitive prices. Increased variety and quality improve consumer welfare and overall living conditions.
Disadvantages of Foreign Direct Investment
Despite its benefits, foreign direct investment is not risk-free. Host countries must monitor and regulate FDI to avoid harmful consequences.
-
Loss of Local Business Competitiveness
Large multinational corporations often have more capital, better marketing strategies, and advanced technology. Domestic companies may struggle to compete and could be forced out of the market. Over time, this may result in reduced industrial diversity and economic vulnerability.
-
Repatriation of Profits
While FDI creates jobs and business activity locally, the profits generated are often sent back to the investor’s home country. If profit repatriation grows excessively, the host nation may experience:
- Reduced national income retention
- Balance-of-payments challenges
- Limited long-term benefit from economic growth
-
Risk of Monopoly or Market Dominance (Advantages and Disadvantages of Foreign Direct Investment)
Some multinational companies can become dominant players in the host market. Their power might allow them to:
- Control prices
- Influence regulations in their favor
- Limit market access for new domestic startups
This reduces economic fairness and competition.
-
Exploitation of Natural Resources and Environmental Harm
Foreign investors may focus on quick profit and exploit natural resources irresponsibly. In countries with weak environmental regulations, FDI projects can lead to:
- Pollution of water, land, and air
- Deforestation
- Resource depletion
- Long-term ecosystem damage
The environmental cost may outweigh short-term economic gains.
-
Economic and Political Dependency
Excessive reliance on foreign investment could weaken national autonomy. Governments may avoid policies that upset multinational corporations, even when such policies are beneficial to citizens.
Political influence from foreign investors might compromise a country’s long-term strategic interests.
-
Job Quality Concerns and Labor Exploitation
Some industries may offer jobs with:
- Low wages
- Poor working conditions
- Limited labor rights protections
This is especially common in low-cost manufacturing or resource-extraction sectors.
-
Cultural and Social Influence
FDI promotes global business practices that can reshape local values and lifestyles. Over time, the dominance of foreign brands may:
- Reduce traditional cultural identity
- Encourage excessive consumption behaviors
- Create inequality between workers employed by foreign vs. domestic firms
These social challenges need to be managed carefully.
Advantages and Disadvantages for Home Countries (of Foreign Direct Investment)
Foreign direct investment not only affects host countries but also influences the investor’s home economy.
Benefits for Home Countries
- Increased global market share and business profits
- Strengthened brand presence and international reputation
- Access to cheaper labor and resources
- Increased royalty and licensing income
- Improved supply-chain efficiency
Successful overseas expansion helps home-country firms stay competitive globally.
Drawbacks for Home Countries
- Potential job losses due to relocation of production
- Reduced domestic investment
- Decline in certain manufacturing sectors
- Economic backlash if foreign investments fail
Governments must ensure that outward FDI supports balanced economic development at home.
Advantages and Disadvantages for Multinational Corporations
FDI is a powerful business strategy, but it requires careful planning.
Advantages for MNCs
- Direct access to new customer markets
- Greater control over operations than licensing or franchising
- Avoidance of trade barriers such as tariffs
- Diversified business risks across multiple countries
- Lower production costs in certain markets
FDI supports long-term profitability and global integration.
Disadvantages for MNCs
- High capital cost and financial risk
- Political instability and policy uncertainty
- Exchange rate fluctuations affecting profits
- Cultural differences complicating management
- Potential backlash from local communities or governments
Multinational companies must assess risks thoroughly before investing abroad.
How Governments Can Maximize FDI Benefits
To achieve sustainable growth, host countries should focus on:
- Strengthening legal and regulatory frameworks
- Enforcing environmental protection standards
- Supporting domestic SMEs to enhance competitiveness
- Encouraging technology absorption through knowledge-sharing policies
- Promoting fair labor practices and worker training programs
- Negotiating balanced agreements to ensure shared value creation
Smart policy design ensures FDI becomes a collaborative force for national prosperity.
Conclusion
Foreign direct investment is a crucial engine of global economic development. It can generate tremendous advantages for host economies through job creation, capital injection, technology transfer, and enhanced trade opportunities. At the same time, it can create risks such as environmental damage, inequality, and over-dependency on foreign companies.
The true impact of FDI depends on how effectively it is managed. Governments must balance openness to foreign investors with strong policies that protect local industries, workers, and long-term national interests. Meanwhile, multinational corporations should invest responsibly, respecting local communities, environmental standards, and fair business principles.
When guided wisely, foreign direct investment becomes a powerful instrument for building innovation-driven, sustainable, and inclusive economies around the world.
Read more:
Find out easiest business to start from home
Best investment Opportunities in Vietnam for the year of 2026